- Home
- Engineering
- Risk-Based Inspection (RBI)
- Heat Exchanger Bundles
HEAT EXCHANGER BUNDLES
Identify Risk Limits & Optimize Turnaround Scope
Many companies predict bundle life by analyzing the history of each heat exchanger (HE) shell and tube. Unfortunately, there’s not enough data to accurately predict future performance or probability of failure (POF) or consider current operating conditions or practices.
A risk-based inspection (RBI) assessment should be conducted on HE bundles to avoid unexpected downtime and lost production and to increase knowledge on bundle deterioration and anticipated life. E2G uses the API RBI methodology to analyze the failure data of similar HE bundles and incorporate the financial consequences of lost production and downtime associated with repair or replacement.
Case Study: Heat Exchanger Bundles using RBI
Background
Approach
E2G evaluated the POF and consequence of failure (COF) to determine the overall financial risk. The POF of bundle RBI is calculated by comparing similar service bundles to determine a characteristic HE bundle’s life. The COF of bundle RBI considered the costs the facility would incur if any HE bundles failed. The COF calculation considered production and environmental impacts and bundle replacement costs. E2G used the bundle’s inspection history to predict POF, COF, and to determine the risk at various times in the future.
Matching criteria included:
- Heat exchanger type
- Tube metallurgy
- Tubeside and shellside fluid categories
- Operating condition, temperature, pressure, and velocity
- Process unit
- Damage mechanisms and fluid damage modifiers
Result
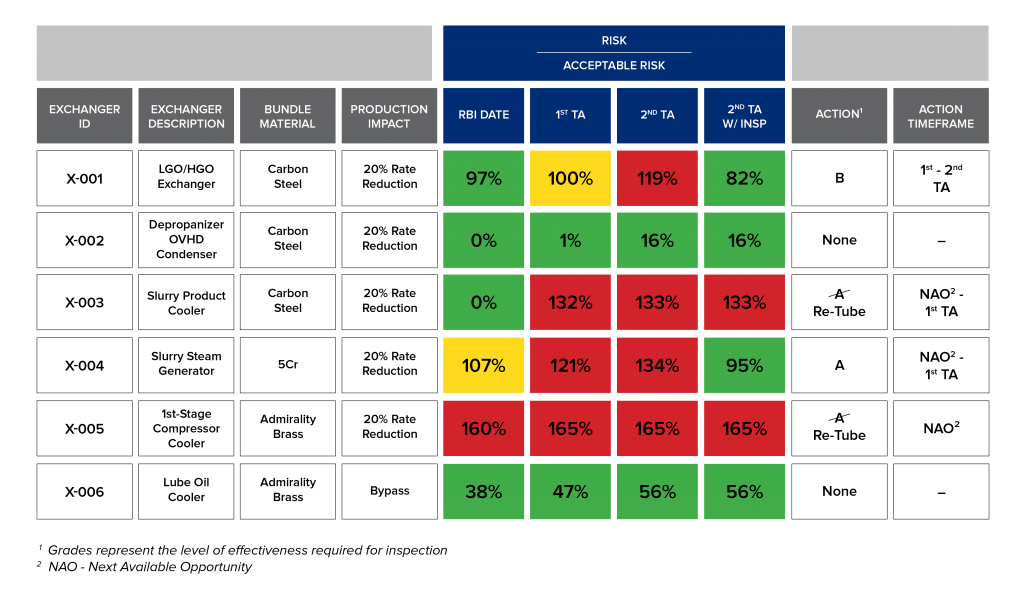
E2G created an inspection plan that highlighted inspection and replacement activity for the bundles. The following recommendations were identified:
- X-002 and X-006 – no inspection required until the second TAR
- X-003 and X-005 – replace bundles at the first TAR, as both are near end of life
- X-001 and X-004 – inspect bundles to extend life to second TAR
- X-004 – replace and inspect at next available opportunity
- X-001 – inspection should be completed between the first and second TARs
By comparing the risk of a bundle to an acceptable financial risk limit, an inspection plan was developed that identified the highest risk HE bundles and delayed two HE bundles until the second TAR. This analysis helped the facility avoid unexpected downtime and lost production, and increased the knowledge on deterioration and anticipated life.
Recommended Reading
- Library /
- Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) /
- Library /
- Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) /
- Library /
- Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) /
RBI Expertise
E2G’s risk-based inspection engineers have supported the implementation of RBI programs for many refining, energy, petrochemical, and chemical facilities across North America. As a pioneer in RBI methodologies, our experts collaborate with E2G’s materials & corrosion experts to deliver the most experienced engineering consultancy for your RBI implementation.
Our experts:
- Have 250+ years of combined field experience
- Have served as API 520 task force chairman for more than 25 years
- Are the lead investigators on API 581
- Developed the only API-branded and fully compliant API 581 RBI software
- Collaborate with E2G’s multi-disciplinary experts to provide practical recommendations